What was the effect of liberalization on India's exports?
Since liberalization our trade foreign trade has expanded manifold and has seen significant structural shifts in product as well as geographic composition. The share of foreign trade (export & import) in India’s GDP stood at 13-15 % against 43% now. Let us see how liberalization has helped exports.
Our Trade has expanded
India, which had a global share of 2.4 per cent in trade at the time of independence, dropped to a mere 0.7 per cent in 1991 because of inward looking policy of self-reliance and exporting only the surplus. The balance of payment crisis in 1991 resulted in opening up the economy and a new foreign trade policy that resulted in India’s two way trade in both merchandise and services reach nearly $ 1 trillion annually from a mere $70-80 billion in 1991. India’s share in global merchandise trade has gone up to 1.7 per cent in 2013-14 from 0.7 per cent in 1991.
During the last 25 years, India’s exports have increased more than 17 times, from US$ 18.1 billion in 1990-91 to US$ 309 billion in 2014-15. In the first decade of this period (1990-91 to 1999-2000), India’s exports grew at a CAGR of 8.1 percent. The real surge was witnessed in the next decade (2000-01 to 2009-10), when exports grew at 16.8 percent annually. This trend continued until 2011-12, after which there has been a steady decline in trade owing to global slowdown.
Exports are more geographically diversified now:
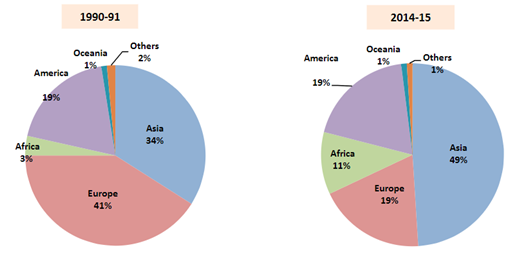
During the initial period of liberalization, India’s exports were less diversified, with top 20 countries accounting for more than 80 percent of India’s total exports. During 1991-92, USA was the largest export destination, today, top 20 export destinations for India account for 67 percent of total exports, reflecting greater diversification. While USA remains the largest export destination, its share has come down to 13.7 percent. UAE has emerged as second largest export destination accounting for 10.7 percent share. The most significant change in the direction of India’s exports during post-liberalization era has been the increasing share of developing countries and falling share of advanced and developed economies.
India’s export by region:
Structural shift in exports basket:
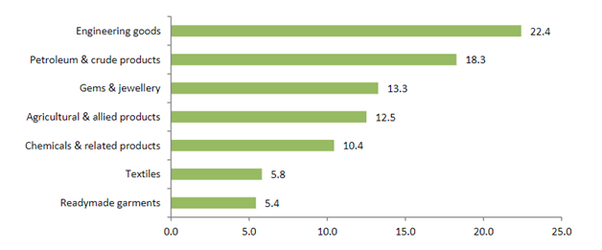
The composition of exports has gone substantial changes since liberalization. There is a structural shift in India’s exports, away from primary, agricultural and traditional exports like textiles towards more value added manufactured and technology-based items such as engineering goods, refinery products, pharmaceuticals, etc. Overall, India’s export basket is now diversified with non-traditional items and differential products are also gaining importance
India’s principle exports:
Source:
1. www.ficci.in/SPdocument/20858/Trends_in_India's_Foreign_Trade
2. http://www.pib.nic.in/newsite/mb...